Natural resources are finite, or at a minimum, can easily be consumed faster than they can be replaced. As such, the conservation of natural resources is a pragmatic endeavor. Geosynthetics—widely available materials used in construction, civil engineering, and environmental protection—can be useful in promoting the conservation of these resources. When used as intended, geosynthetics can enhance soil properties and reduce the demands placed on natural resources.
Types of Geosynthetics
Geosynthetics are typically made from synthetic polymers, such as polyethylene, polypropylene, and/or polyester, and are designed to be durable and resistant to weathering and other environmental factors.
General groupings of geosynthetics include geotextiles, geogrids, geomembranes, geocells, erosion control blankets (ECBs), and turf reinforcement mats (TRMs).
Geotextiles (permeable) and geomembranes (impermeable) provide separation, while geogrids and geocells provide varying degrees of stabilization and confinement. ECBs and TRMs, made with a combination of natural and synthetic fibers, resist surficial erosion by preventing seed washout prior to germination.
Application areas where these geosynthetic materials are used typically include load support; slope, shoreline and channel protection; and earth retention.
Using Geosynthetics in Load Support Applications to Conserve Natural Resources
In load support applications, geogrids, geotextiles, and geocells can all be used to reduce structural cross-section depths, thereby conserving natural resources. The figure below illustrates this benefit and provides a comparison of four structurally equivalent unpaved road sections over a very weak subgrade with a CBR of 0.5%.
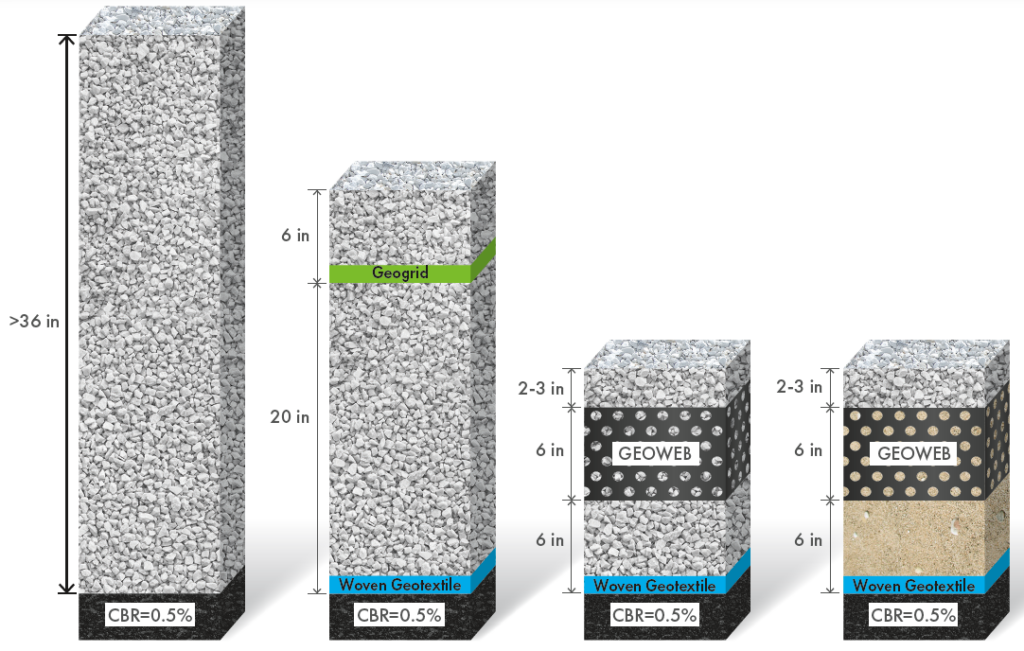
As shown, the conventional cross-section in this case would require more than 36 inches of aggregate to achieve minimal stability, while the planar geosynthetic option (geogrid + geotextile) would require 26 inches of aggregate. Most notably in this case is that geocells—specifically the GEOWEB® Geocells—can be used to achieve an optimal section thickness of only 15 inches, and where suitable on-site material (OSM) is available, it is possible to limit imported aggregate to just the wearing course.
How Geocells Conserve Natural Resources
Through full-depth confinement, geocells allow for the use of lower-quality, non-cohesive soils and recycled materials (concrete, asphalt), further conserving resources through beneficial reuse. Beneficial reuse of any of the aforementioned reduces imported material requirements, thereby conserving aggregate, and with the additional benefit of less truck traffic to the site, conserves oil and gas and puts less stress on local roadways. Properly designed geosynthetics can also increase your roadway´s useful life and reduce or eliminate maintenance needs.
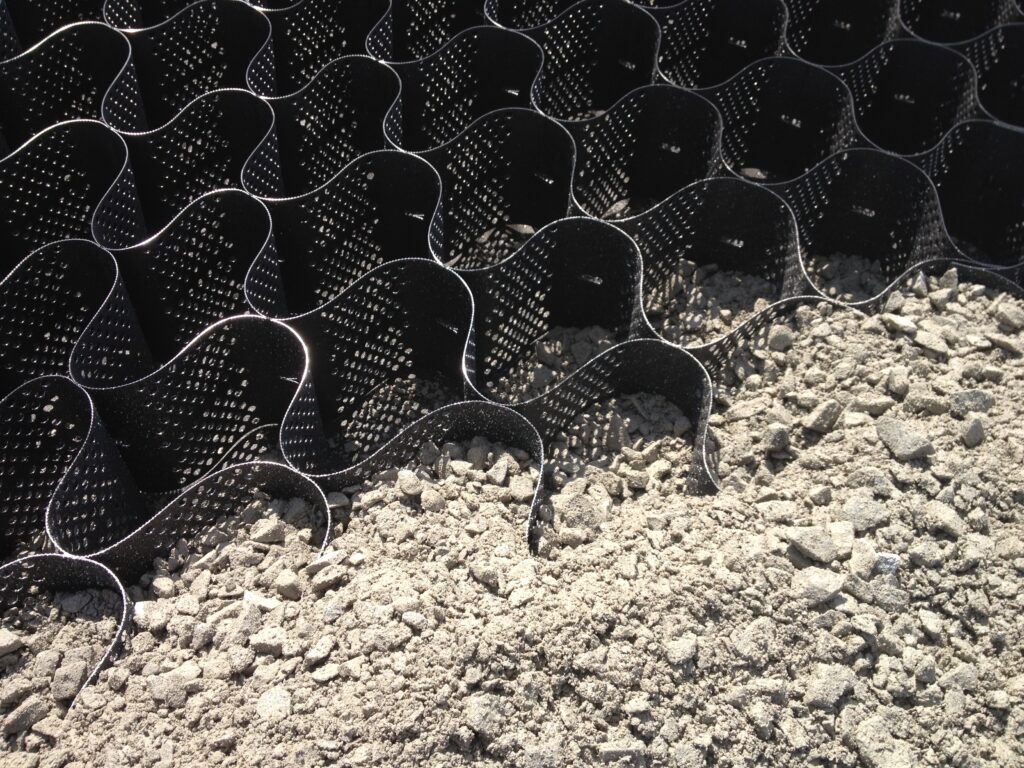

In slope, shoreline, and channel applications, ECBs, TRMs—and to a further extent—geocells, help prevent surficial soil erosion—a process that can cause significant damage to natural ecosystems and lead to the loss of valuable topsoil. While ECBs and TRMs are suitable to protect the surface, adding geocells to the cross-section can prevent supersaturated soils below these products from washing downslope or downstream, and can improve the hydraulic performance of the materials used in the geocells.
Finally, geosynthetics can be used in constructing retaining walls and embankments, which can help conserve resources by reducing the need for land excavation and fill. In retaining wall construction, geogrids—and occasionally geotextiles—are used as tiebacks in Mechanically Stabilized Earth (MSE) structures, while geocells and TRM wraps are just a few of the many different geosynthetic facing options available. Geocells can not only be used to create living green walls to help stormwater infiltrate naturally and add an aesthetically pleasing finish to a structurally sound engineering solution, but research has also shown that geocells can withstand high levels of seismic shaking and may be a suitable option in many earthquake-prone parts of the world.
Presto Geosystems’ engineering team works closely with its customers to provide free project evaluations, with engineering support from the preliminary stages through construction. The project evaluation will deliver a technically sound, cost-effective solution based on four decades of accredited research and project experience. Responsible use of engineered materials designed for long-term performance in the environment can help achieve a more sustainable approach to construction. Written by Cory Schneider, environmental scientist, Presto Geosystems.
 TEXTILES.ORG
TEXTILES.ORG


